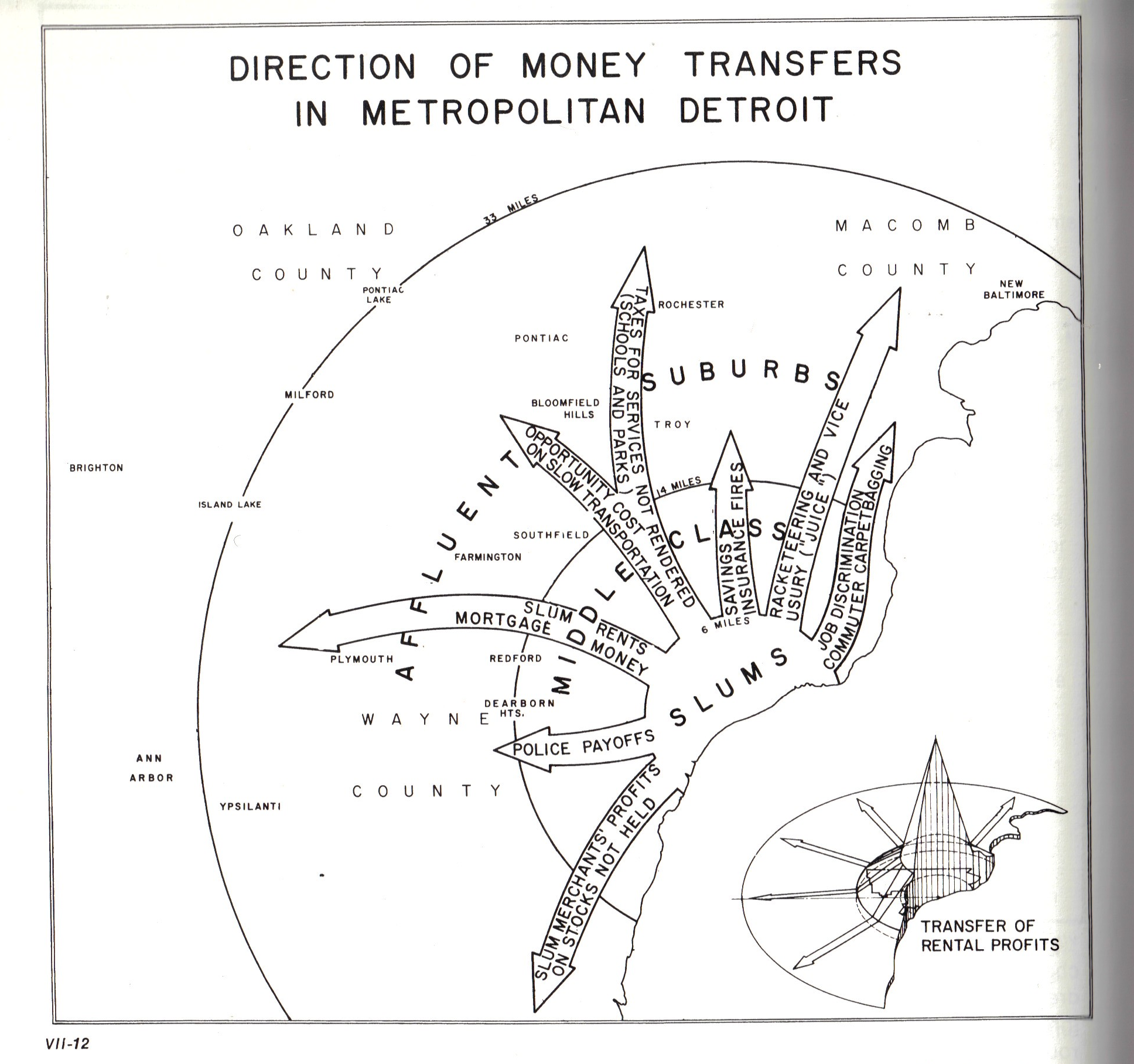
 Bill Bunge
Bill Bunge
Welcome to Advanced GIS, Lecture 1
This is a web page that can be viewed as slides.
→ to move forward
← to go back
for International Crises, Development and the Environment
latitude and longitude
projections
raster vs vector
raster

vector
vector
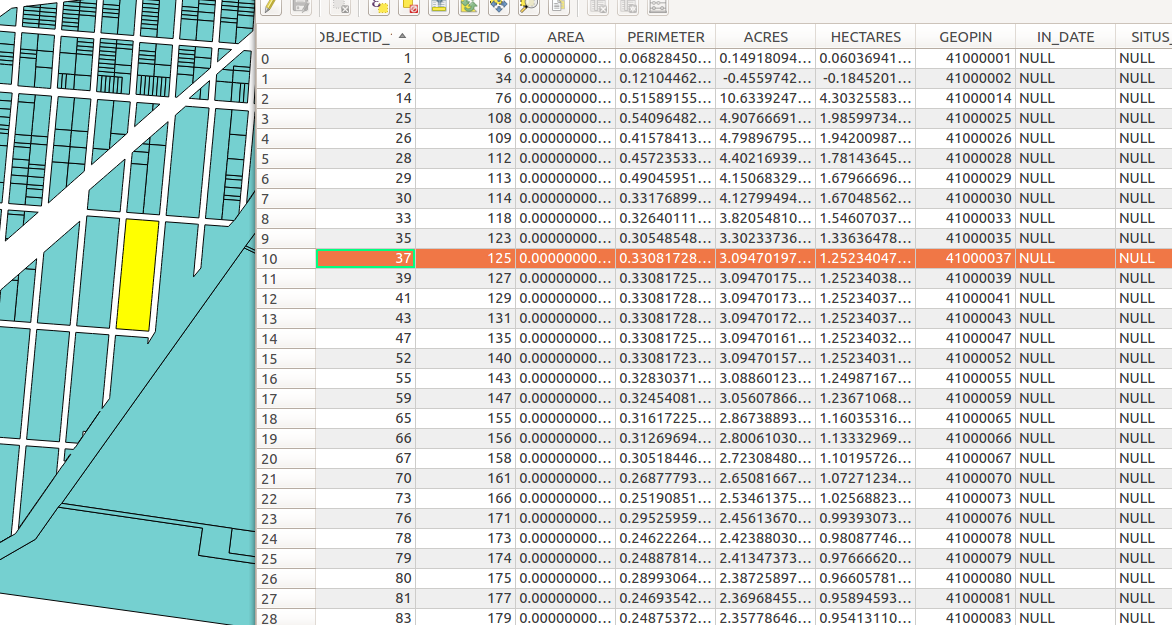
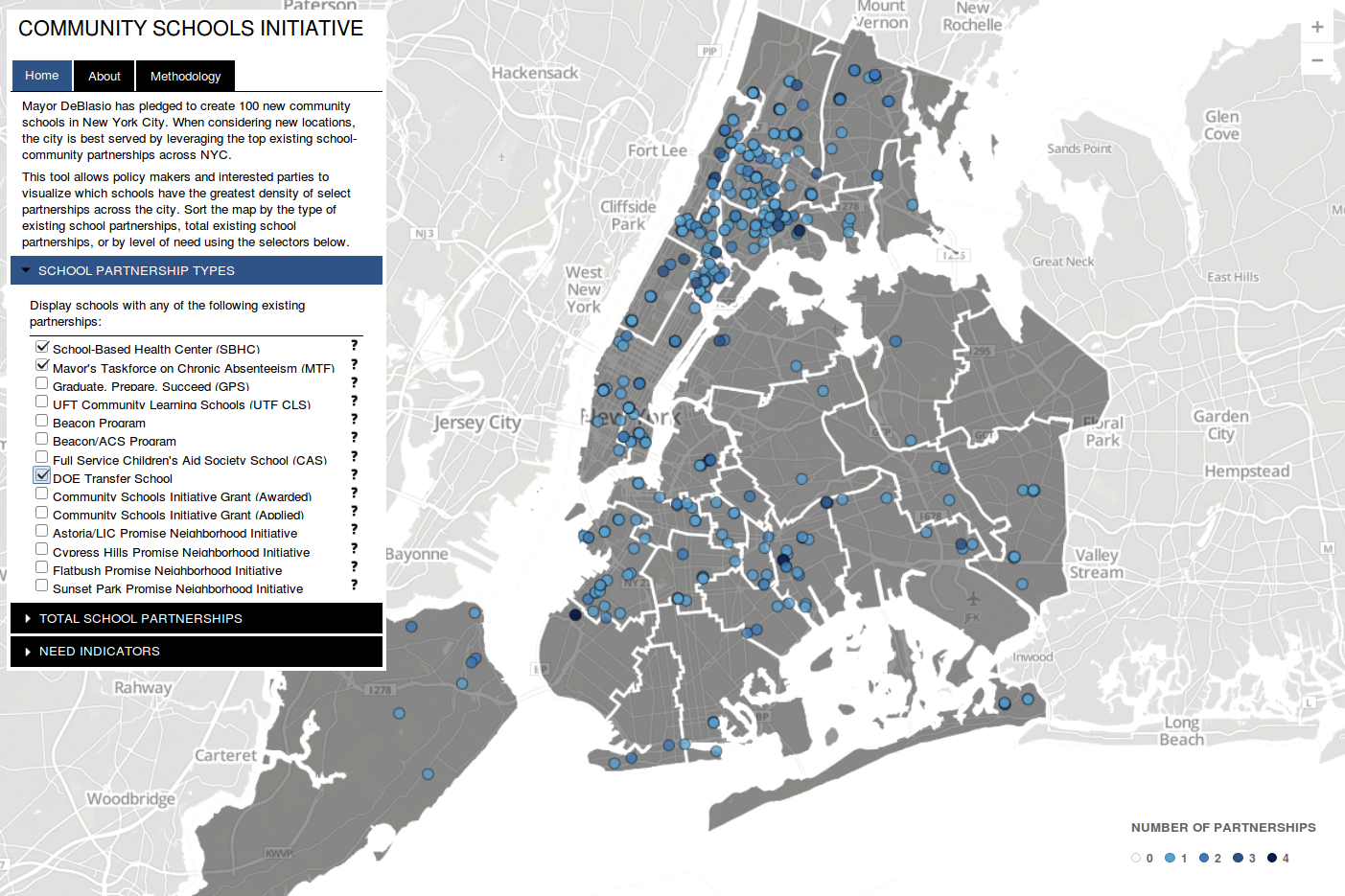
GIS
Geographic Information System
Geographic Information Systems

shapefile
shapefile
.shp
shapefile
.shp
(.zip)
shapefile
shapefile

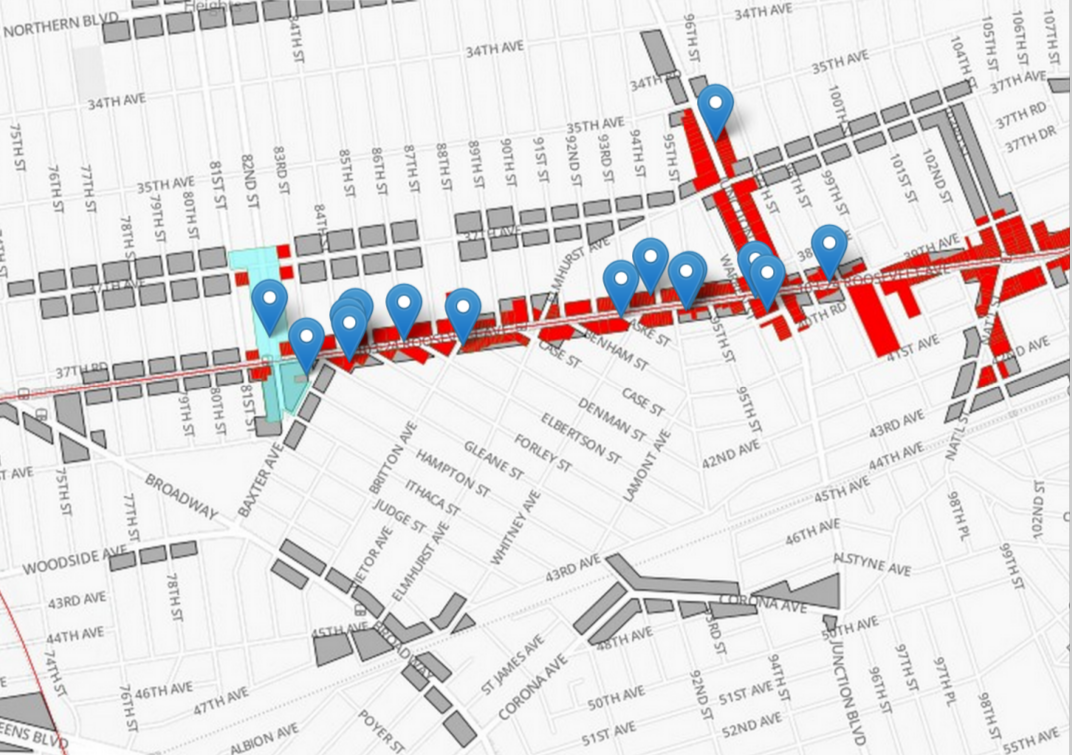
clipping
clipping
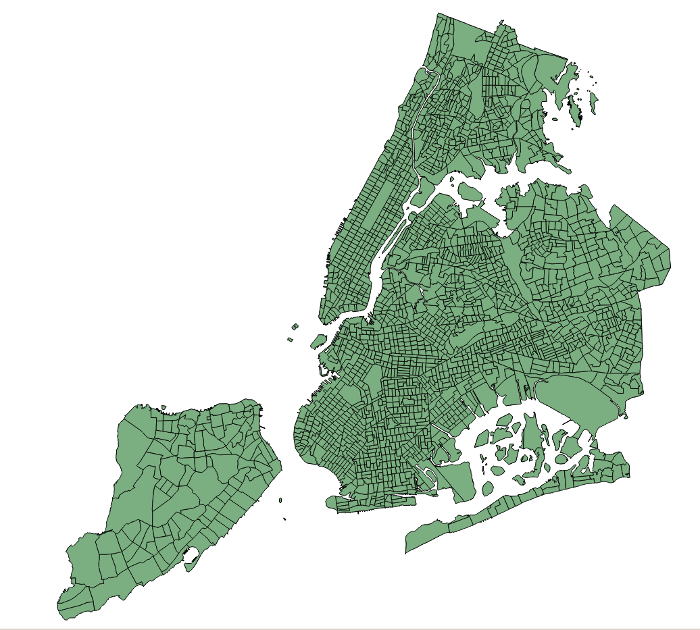
clipping
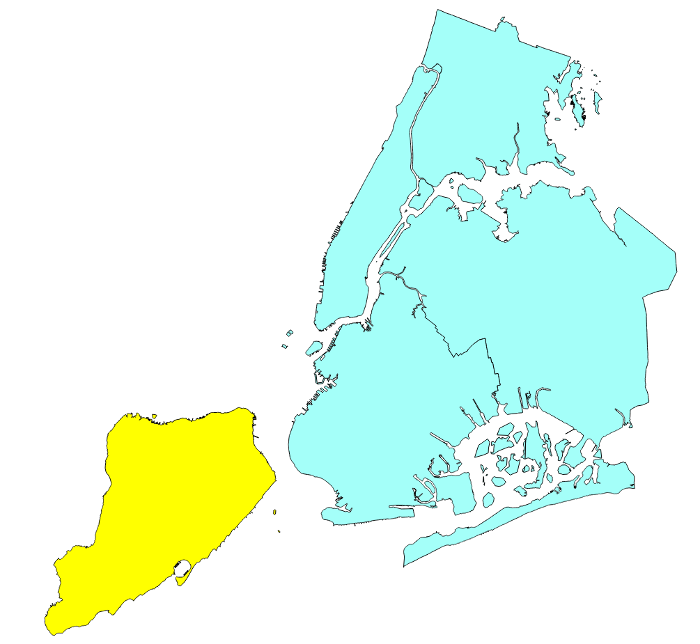
clipping
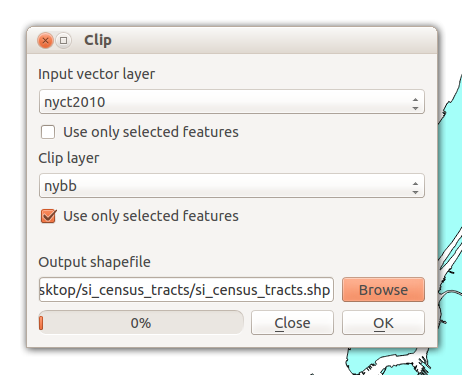
clipping
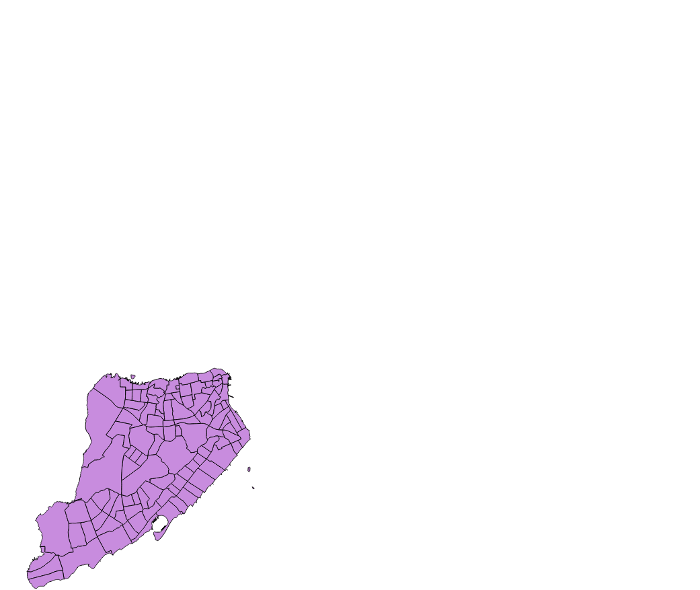
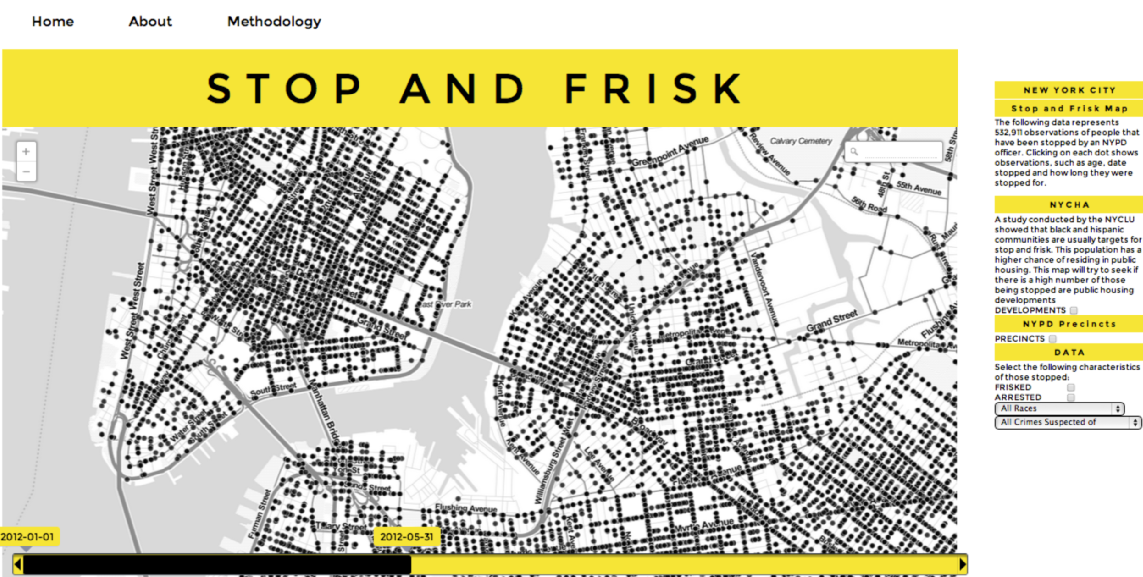
What do you think of when you think of a "modern" map?
the set of practices and software that bring maps to the web and the maps that are their outcomes
platforms for working with maps and data
(open) data
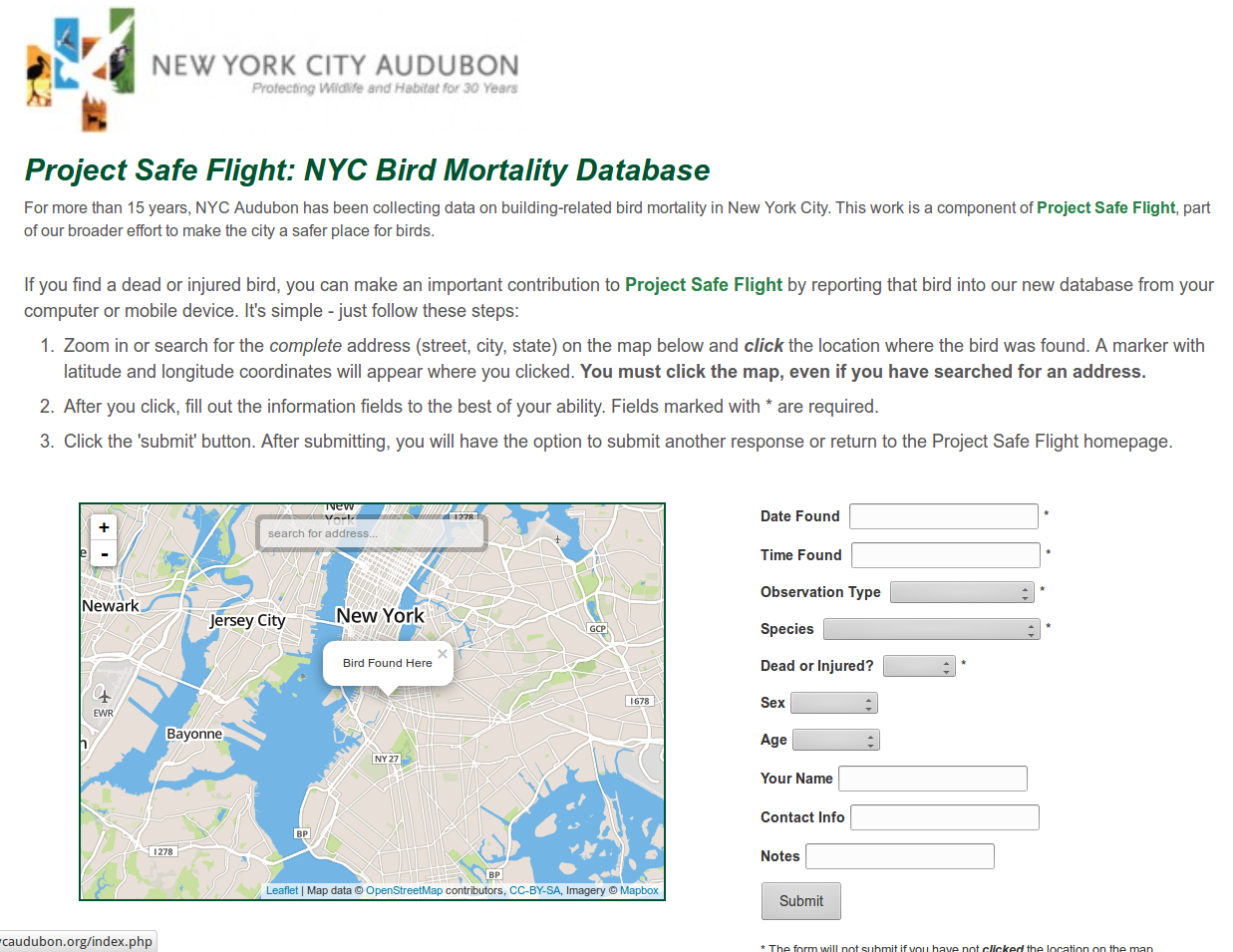
adding spatial data to otherwise non-spatial artifacts
(eg, geotagging of pictures on a service like flickr, adding location to tweets, etc)
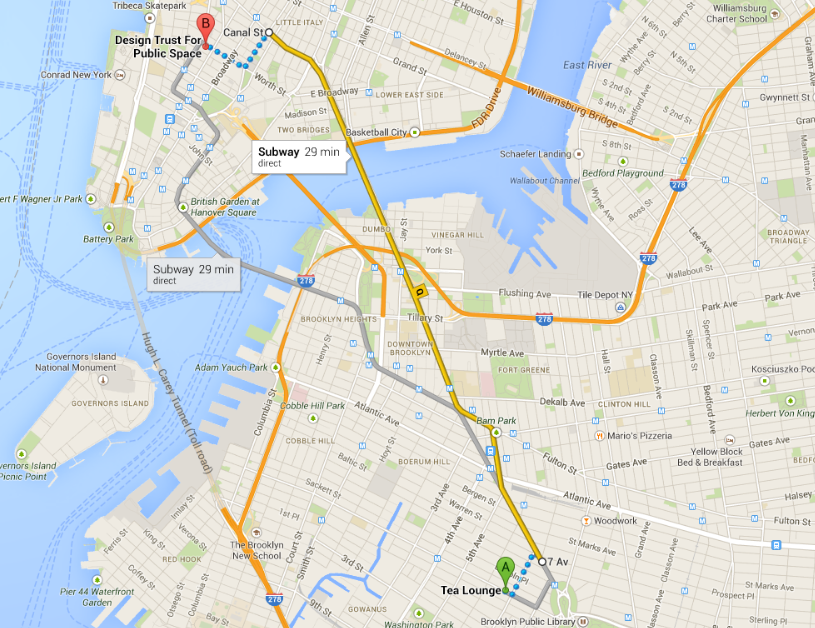


click

click
...wait

click
...wait
entire page reloads,
map is panned east


(Asynchronous Javascript and XML)
(Asynchronous Javascript and XML)
dynamically loading portions of webpages
not really new, but newly articulated
can be seen just about everywhere now, but eg, 596 Acres
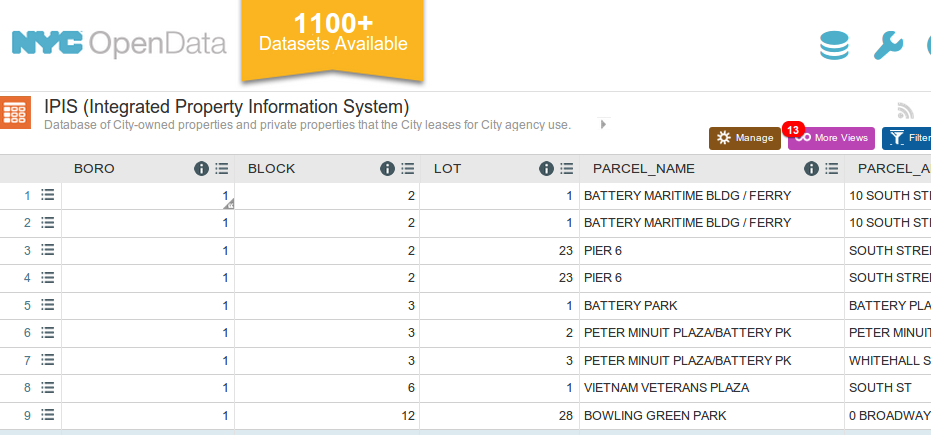


source code


Linux taken seriously by Microsoft (~1998)
"Recent case studies (the Internet) provide very dramatic evidence ... that commercial quality can be achieved / exceeded by OSS projects."
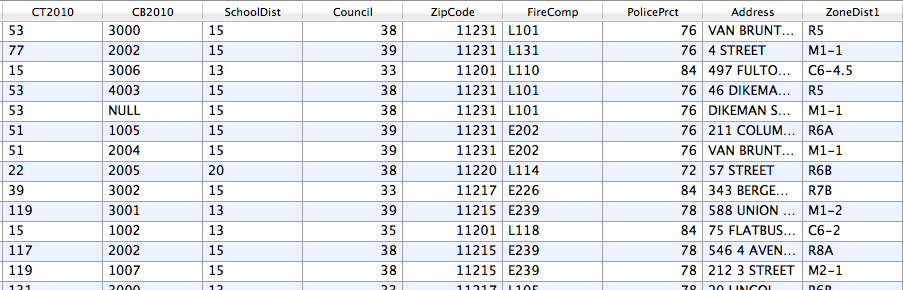
1. Start with some data

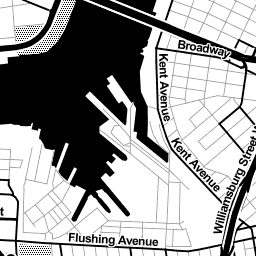
2. Make or reuse base tiles
Street, water and land data
Street, water and land data →
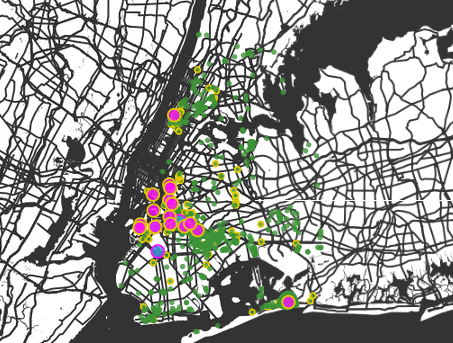
3. Overlay data

4. Mix with some html, css, and javascript
1. Start with some data
2. Make or reuse base tiles
3. Overlay data
4. Mix with some html, css, and javascript